Boils
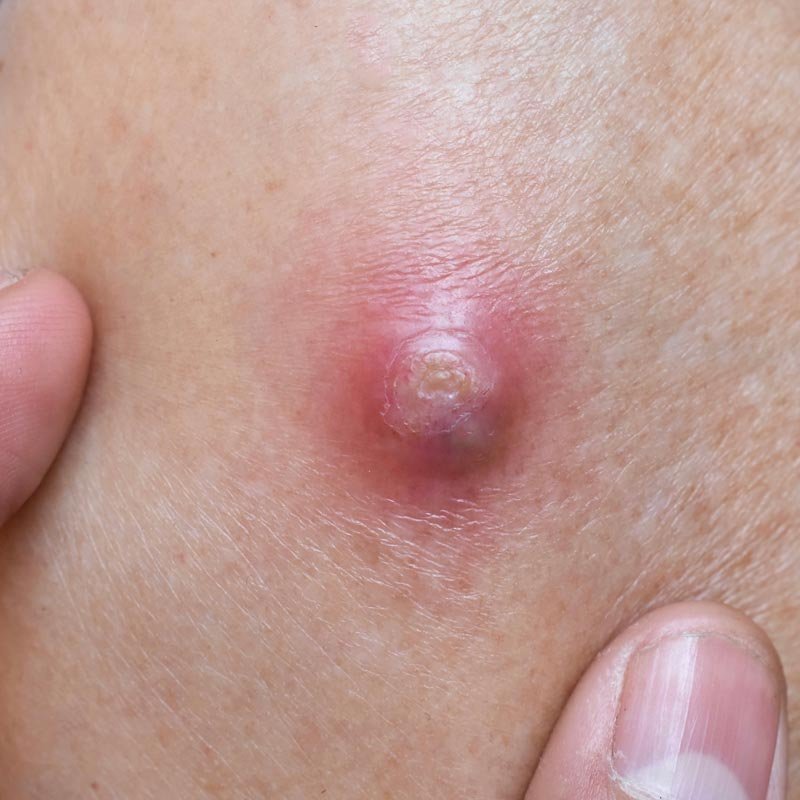
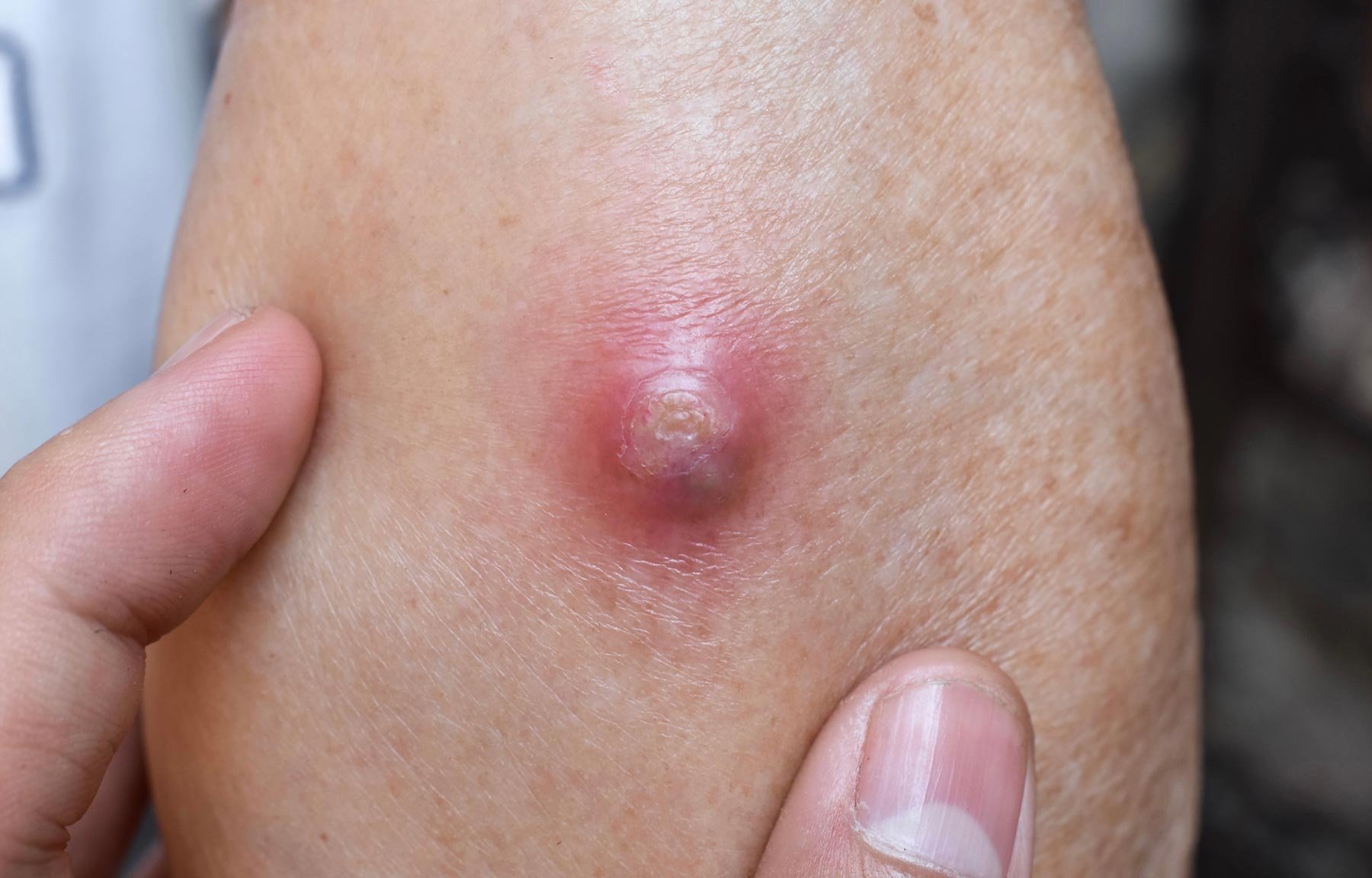
A boil, also known as a skin abscess, is a painful, pus-filled infection that typically develops on the skin or in the hair follicles. Boils are caused by a bacterial infection, most commonly by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. They can develop anywhere on the body, but are most commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, buttocks, and thighs.
Boils typically begin as a red, painful bump on the skin that may be swollen and warm to the touch. Over time, the bump will fill with pus and may become larger in size. Boils can range in size from a small pea to a large golf ball, and may take several weeks to fully develop and heal.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing boils, including:
Poor hygiene
Weakened immune system
Diabetes
Poor nutrition
Using poor-quality or dirty needles
Sharing personal items such as towels or razors
Boils can be uncomfortable and can cause a significant amount of pain, especially if they are large or located in an area that is prone to movement or pressure. They can also lead to scarring if not treated properly.
Treatment for boils involves draining the pus and bacteria from the abscess. This can be done by your dermatology provider and involves making a small incision then gently squeezing the pus out. The area may then be packed with a sterile dressing to help prevent infection and promote healing. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to help kill the bacteria and prevent the infection from spreading.
In some cases, boils may recur or may require more aggressive treatment, such as surgery, if they are particularly large or if they do not respond to other treatment methods.
To prevent boils, it is important to practice good hygiene, including washing your hands frequently and keeping cuts and abrasions clean and covered. Avoid sharing personal items such as towels and razors, and avoid using poor-quality or dirty needles. If you have a compromised immune system, it is important to take steps to strengthen your immune system and prevent infections.
By following these precautions and seeking treatment as needed, you can help to prevent and manage boils and reduce the risk of scarring and other complications.