Hidradenitis Suppurativa
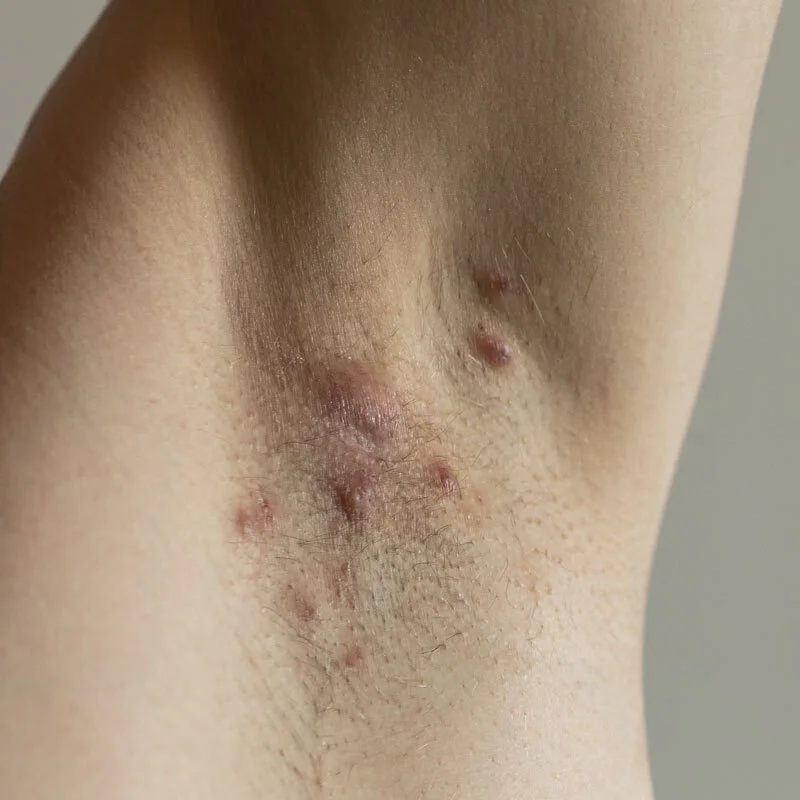
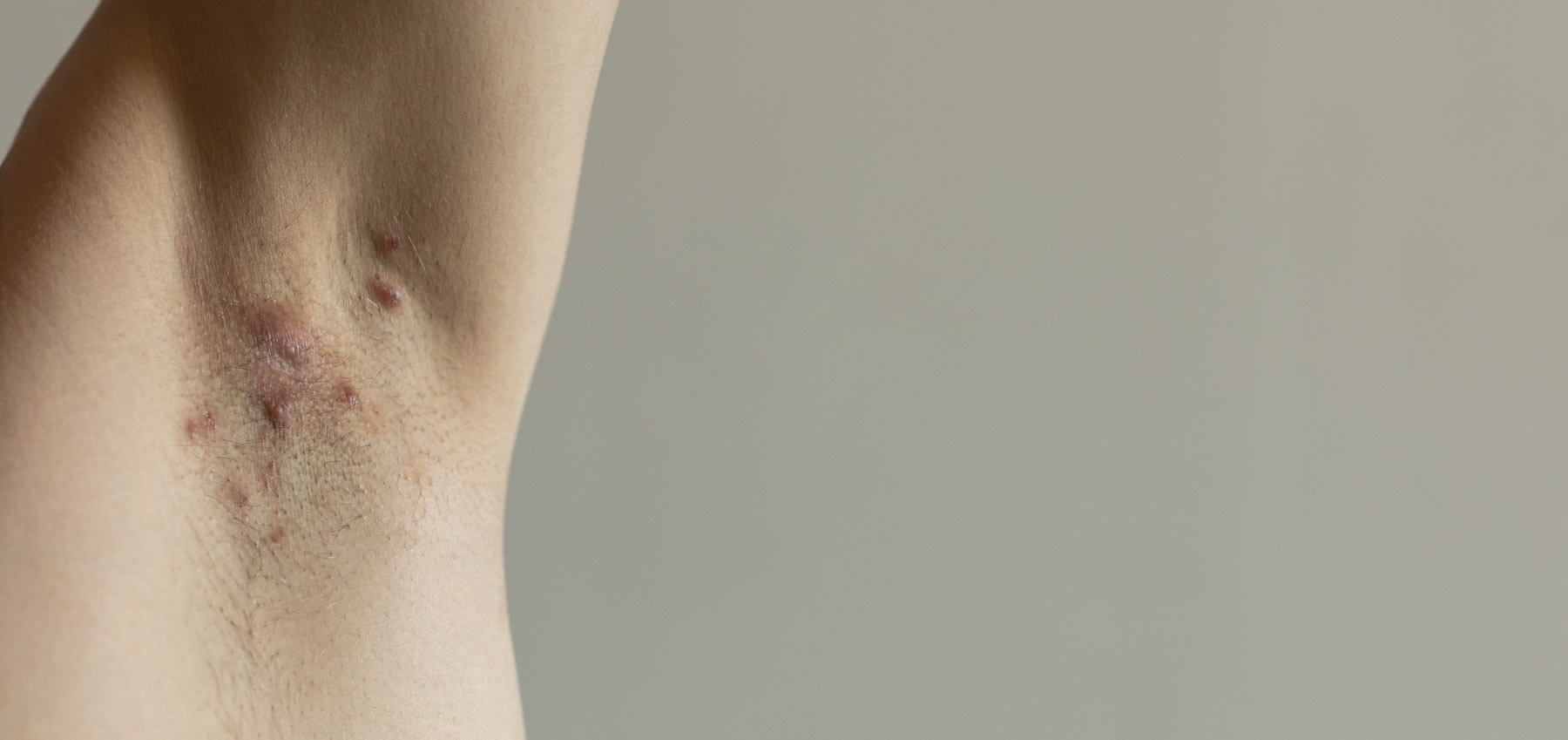
Hidradenitis suppurativa, also known as acne inversa, is a chronic skin condition characterized by the formation of abscesses and scarring in the hair follicles. It typically affects the armpits, groin, and buttocks, but can also occur in other areas of the body such as the breasts and inner thighs. The condition is more common in women than men and usually appears in people between the ages of 20 and 40.
The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is not known, but it is believed to be the result of a combination of factors such as genetics, hormonal imbalances, and certain lifestyle factors such as obesity and smoking. The condition is not contagious and is not caused by poor hygiene.
Symptoms of hidradenitis suppurativa may include the formation of painful, tender lumps or abscesses in the affected areas, drainage of pus or blood from the lumps, and the development of scarring. The lumps may also become chronic and persist for long periods of time.
Diagnosis of hidradenitis suppurativa is usually made through a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. A biopsy may also be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa may include a combination of medications, surgery, and lifestyle changes. Medications may include antibiotics to treat or prevent infections, and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and pain. Surgery may be necessary to remove abscesses or scar tissue, and lifestyle changes such as weight loss and quitting smoking may help to improve the condition.
Hidradenitis suppurativa can be a chronic and recurrent condition, and treatment may not completely eliminate the condition. However, with proper treatment and management, the symptoms of hidradenitis suppurativa can be controlled and the risk of complications can be minimized.