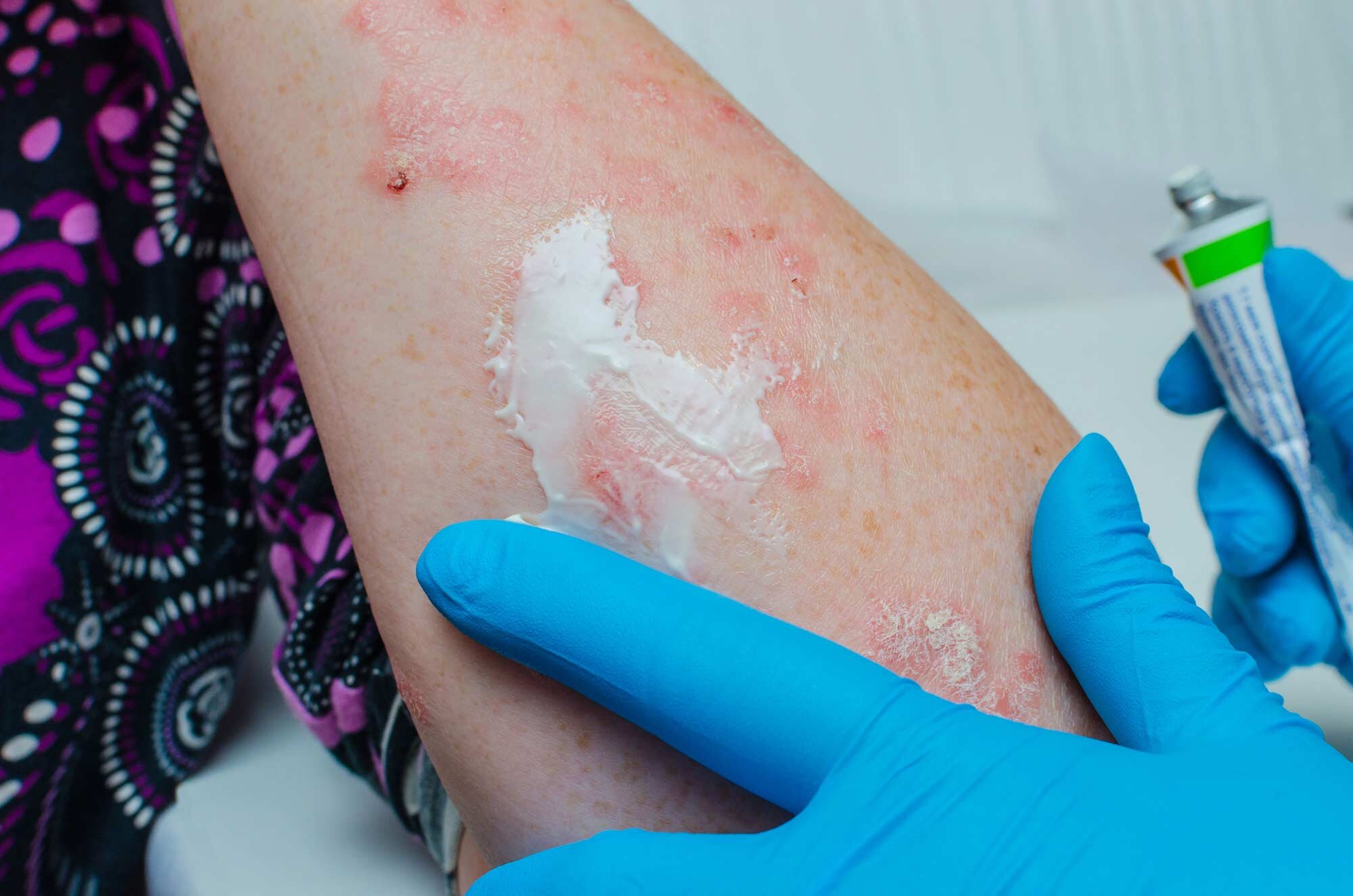
Topical Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
In addition to cryotherapy and surgery, topical chemotherapy and topical immunomodulators (i.e. 5-fluorouracil, imiquimod, or ingenol mebutate) can treat actinic keratoses (precancerous spots) as well as some basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma subtypes. If the skin cancers are fairly shallow and/or numerous, topical chemotherapy cream may be chosen for ‘field therapy.’ The medicated cream is applied daily for a prescribed period of time, generally ranging from 2 to 3 weeks for precancerous lesions to 4 to 6 weeks for early thin skin cancers. Since the medicine is applied topically, the risk of systemic side effects is minimal.
Another option for treating basal or squamous cell carcinomas is injected chemotherapy, such as methotrexate or 5-fluorouracil. These medications have been shown to stop the growth of certain skin cancers when injected directly into the lesions. As with surgery, chemotherapy injections are done in the office.

