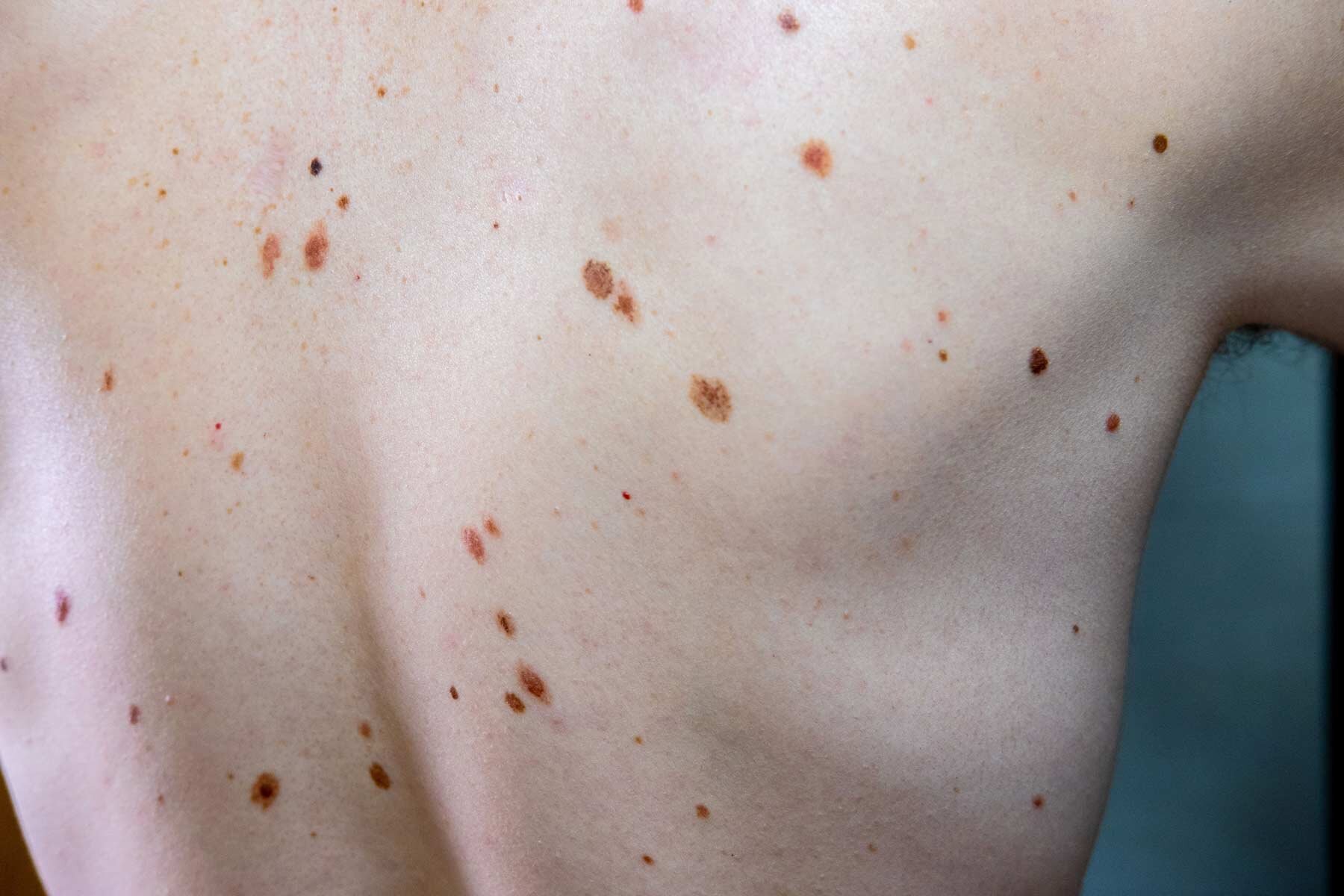
Atypical Moles
Atypical moles, also known as dysplastic nevi, are moles that are larger and have irregular features compared to typical moles. They may be asymmetrical, have uneven borders, and have a mix of colors, including pink, red, brown, and black. Atypical moles are generally benign (noncancerous), but they have a slightly increased risk of developing into melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
It is important to monitor atypical moles and any changes in their appearance, as early detection and treatment of melanoma can be critical to a positive outcome. It is recommended that individuals with atypical moles have regular skin exams by a dermatology provider and perform self-exams at home to check for any changes in their moles.
If you have atypical moles, it is important to protect your skin from the sun to reduce the risk of melanoma. This includes wearing protective clothing, applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and seeking shade when the sun is strongest. It is also important to avoid tanning beds, as the UV radiation from these devices can increase the risk of skin cancer.
If you notice any changes in an atypical mole or any other mole, such as changes in size, shape, color, or texture, it is important to see a dermatology provider as soon as possible. Other warning signs of melanoma include the development of a new mole, itching or bleeding of a mole, or a mole that becomes painful or tender.
Atypical moles can be removed in office for cosmetic or medical reasons. If you decide to have an atypical mole removed, it is important to choose a qualified dermatology provider and to follow their instructions for aftercare to ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of infection.
By monitoring atypical moles and taking precautions to protect your skin from the sun, you can help to reduce your risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. It is important to be proactive in your skin health and to seek medical attention if you notice any changes in your moles or skin.

