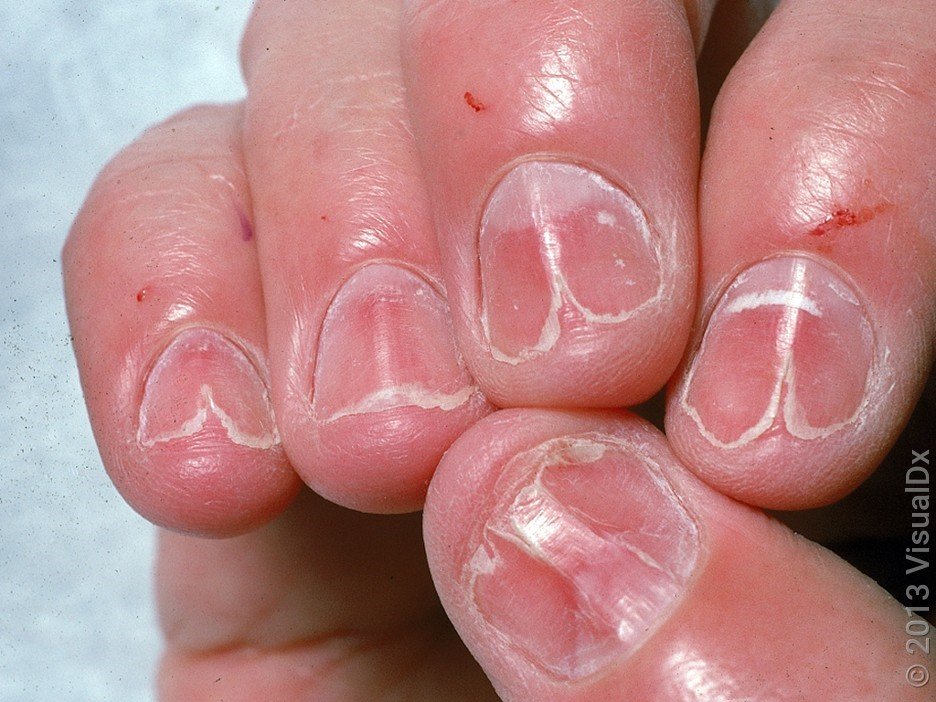
Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is a chronic autoimmune disease that is characterized by the development of inflamed, purple or red, itchy rash on the skin and mucous membranes. Lichen planus can affect any part of the body, but it most commonly appears on the wrists, ankles, lower back, and genitals. The cause of lichen planus is not fully understood, but it is thought to be the result of an abnormal immune response to an unknown trigger. Lichen planus is not contagious and is not caused by poor hygiene.
Symptoms of lichen planus may include the development of a rash on the skin or mucous membranes, such as the mouth or genitals, as well as itching and burning sensations. The rash may be accompanied by the development of white, lacy patches on the skin. In severe cases, lichen planus may cause scarring and changes in the color and texture of the skin.
Lichen planus is diagnosed through a combination of a physical examination and a biopsy of affected skin. A biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of skin for laboratory analysis.
Treatment for lichen planus may involve the use of medications, such as corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation and control the immune system. In severe cases, treatment may also involve the use of immunosuppressive drugs or light therapy. It is important to follow the recommendations of a healthcare provider and to take medications as directed to control the symptoms of lichen planus and prevent complications.